Common Form Runtime
All forms on all GenHelm-built sites are processed using a common form management framework. This ensures that all forms will be processed consistently including handling for all important form functions such as field validation, upload and email support, reCAPTCHA handling, responding to buttons, et cetera.
Forms are page-oriented models so they can be used to render pages in their entirety. Alternatively, forms can be rendered as components of other pages or as part of a layout by referencing the form within a $page function. Forms can be built in sections which can be combined or nested to create larger forms. Forms can also be used as the content to be sent within contact emails.
Form Example
Here we show the form definition used to build the order page on this site. Colon (:) introduces a field and double colon (::) will be substituted for the label attribute of the adjacent field. In this example, there are three other form definitions that make up the complete form; these are referenced using $page functions.
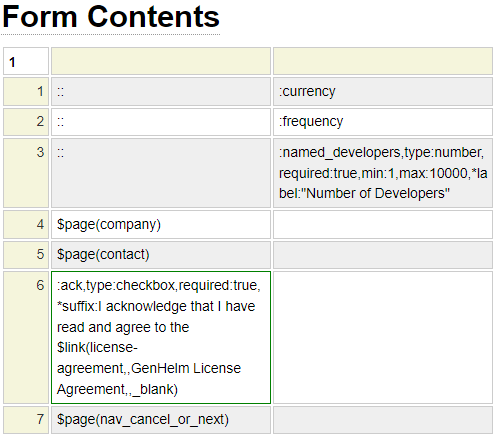
Notice, in the form definition above, there are no details shown for fields currency and frequency. This suggests that these fields have been predefined using the html_field model. Here we see the definition for the currency field.
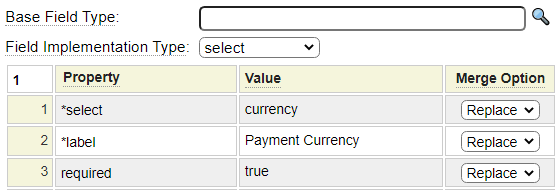
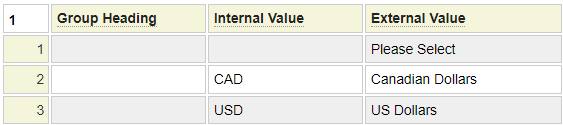
We can see that this field is implemented as a select field. The pseudo property *select references the name of the select definition generated using the select model. Here we show the currency select definition.
Forms can reference other generated components such as form_handlers and transactions as shown here:
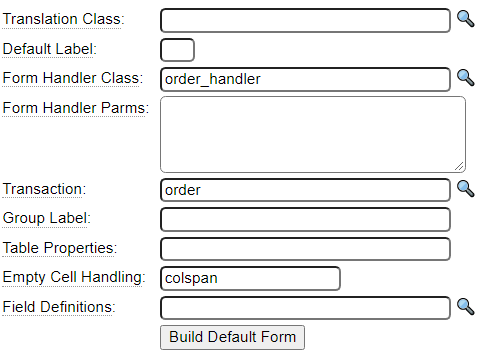
Form handlers are not needed for simple contact forms, for which you only want to send contact details to a site owner via email. Form handlers interact with the form to handle validation and business logic. Here we show the post method of the form_handler associated with the order form above.
function post() {
$country = $this->field_list['country']->value();
$currency = $this->field_list['currency']->value();
$frequency = $this->field_list['frequency']->value();
$state = $this->field_list['state']->value();
$developers = $this->field_list['named_developers']->value();
// Add the order to the cart
$cart = $this->site->create_object('cart','',true);
$cart->set_currency_code($currency);
$behavior['single'] = true; // Only allow 1 item of this type in the cart
$behavior['include_in_item_count'] = 1; // Count as 1 item
$cart->set_item_behavior('license',$behavior);
$license_obj = $cart->create_pending_object('product_license','genhelm-license','license');
$license_obj->set_quantity($developers);
$license_obj->set_frequency($frequency);
$cart->commit_pending_object();
return true;
}Transactions are used for three main purposes.
- To automate the navigation between a series of forms.
- To perform overarching validation involving fields from multiple forms.
- To automatically perform common activities after the completion of the forms that make up the transaction.
Here we show the transaction model specification associated with the order form above.
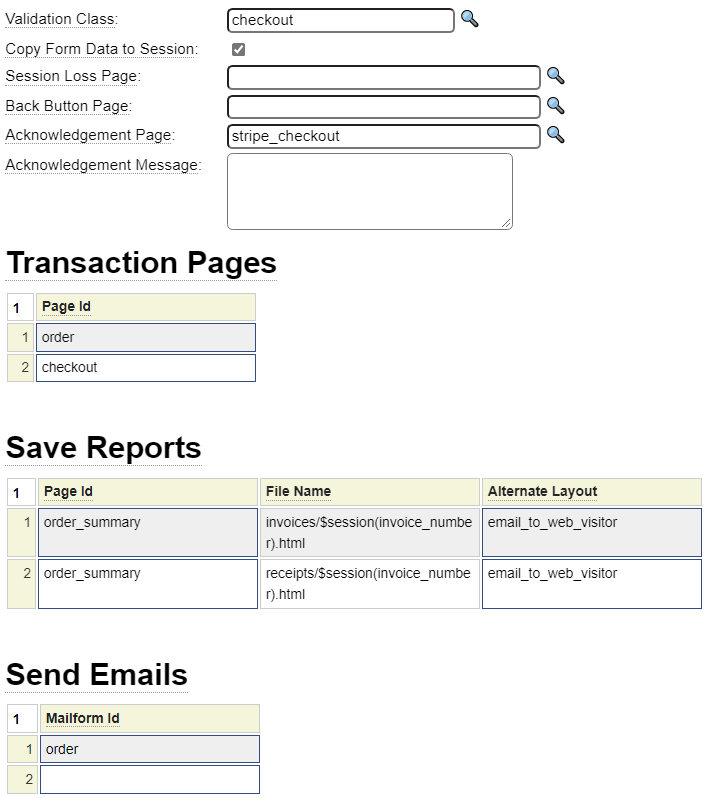
Notice that there are two pages referenced as part of this transaction; the order page shown above as well as a checkout page. The transaction object handles the navigation between these two pages.
When the user completes the transaction, by submitting the last page in the series, the transaction object will automatically perform these steps based on the transaction definition above.
- First, the referenced PHP class, named checkout will be called to perform any validation pertaining to the transaction. If this validation fails, checkout processing will be prevented.
- The transaction will save two reports representing the invoice and sales receipt.
- The order will be sent via email to recipients indicated on the order mailform object.
- The user will be directed to the acknowledgement page identified as stripe_checkout.
Here we show the definition entered in the mailform model to handle the sending of emails.
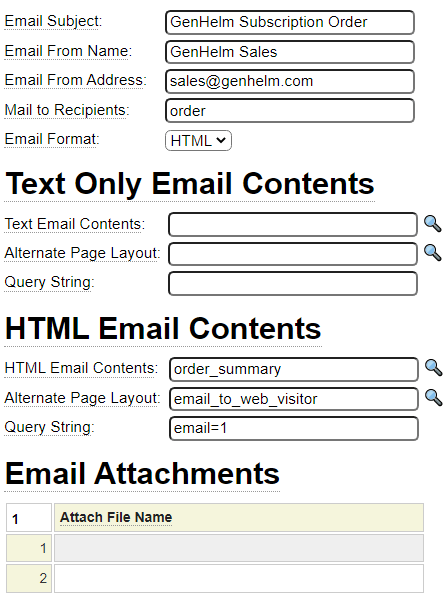
Follow the links below to learn more about the models described above as well as other models that are used to help you build and process forms.
Form-Oriented Models
- This first group of models are used to create various types of field definitions to be added to forms.
- html_field_type is used to define field types, such as birthday, zip_code, phone_number, etc. that can be inherited by any number of form fields.
- html_field is used to define any HTML form field.
- select is used to define select controls.
- select_db_column_values builds dynamic select fields that are associated with a database table column.
- flexgrid generates a flexgrid control which is used to enter 2-dimensional data on a form, much like a spreadsheet.
- form is used to define the look and feel of your form by arranging the form fields and other form content.
- form_handler generates a PHP class that is used to interact with form values to perform things like data validation and button handling.
- mailform is used to define email content that can be sent when a form is submitted. For example, if a user fills out a contact form on your site, their details can be sent to your admin staff via email.
- recipients is used to configure groups of users who should receive various types of emails defined by the mailform model.
- report can be used to save a tab-delimited file containing content generated by submitted forms. For example, historical lists of all contacts.
- transaction is used to link several forms together and automate scrolling between forms. They can also trigger events to be performed after a series of forms have been completed.